前言 Introduction
OpenGL 是一种跨平台的图形编程接口,用于开发二维和三维图形应用程序。它提供了函数和状态机,用于绘制复杂的图形场景、渲染图像和处理用户输入。OpenGL 利用图形硬件加速,通过图形管线处理图形渲染过程。它支持多种图元类型、光照模型和材质属性,并提供着色器编程功能。OpenGL 是广泛应用于图形应用程序和游戏引擎的标准选择,具有跨平台性和强大的社区支持。
效果展示 Presentation
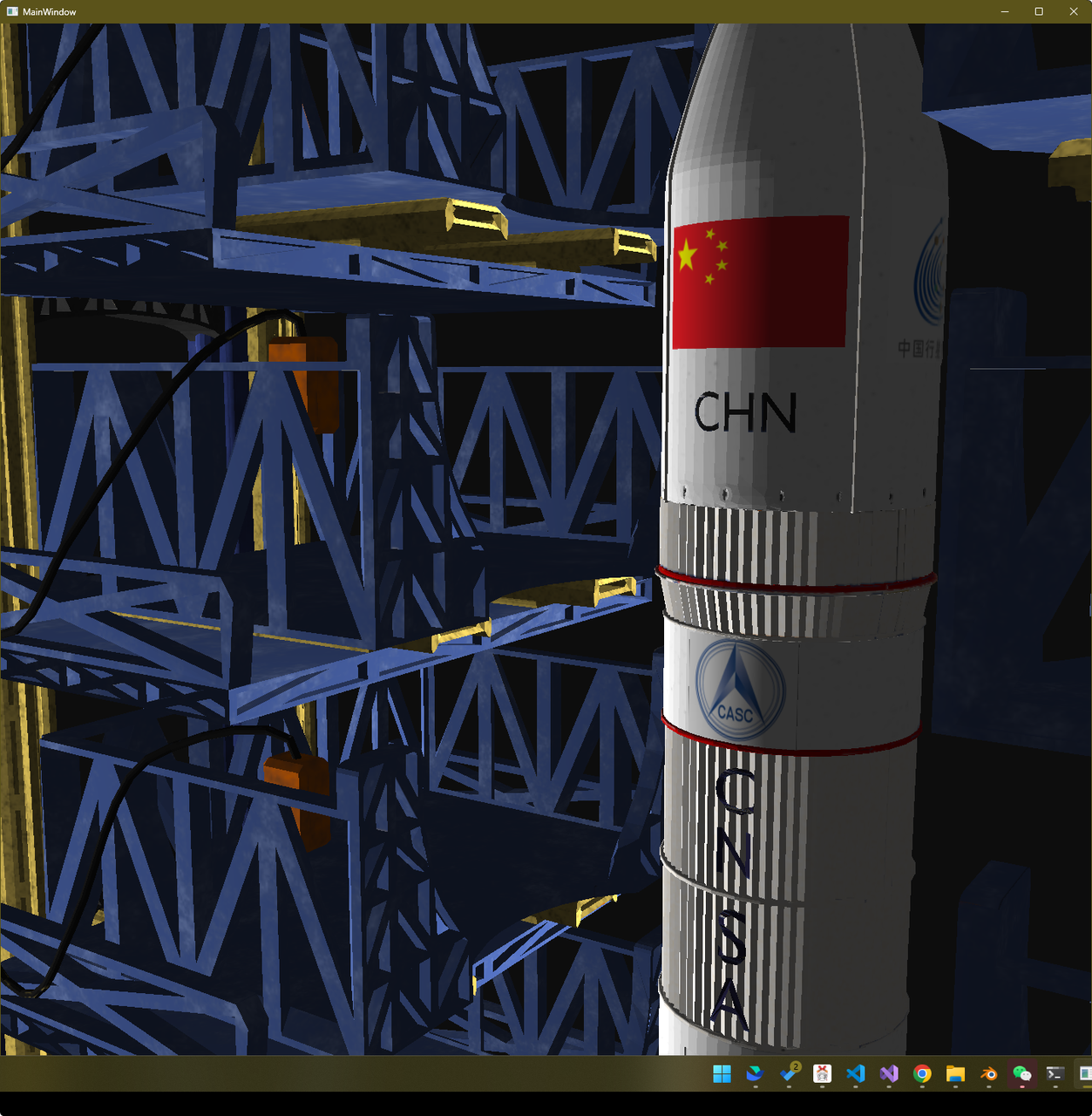
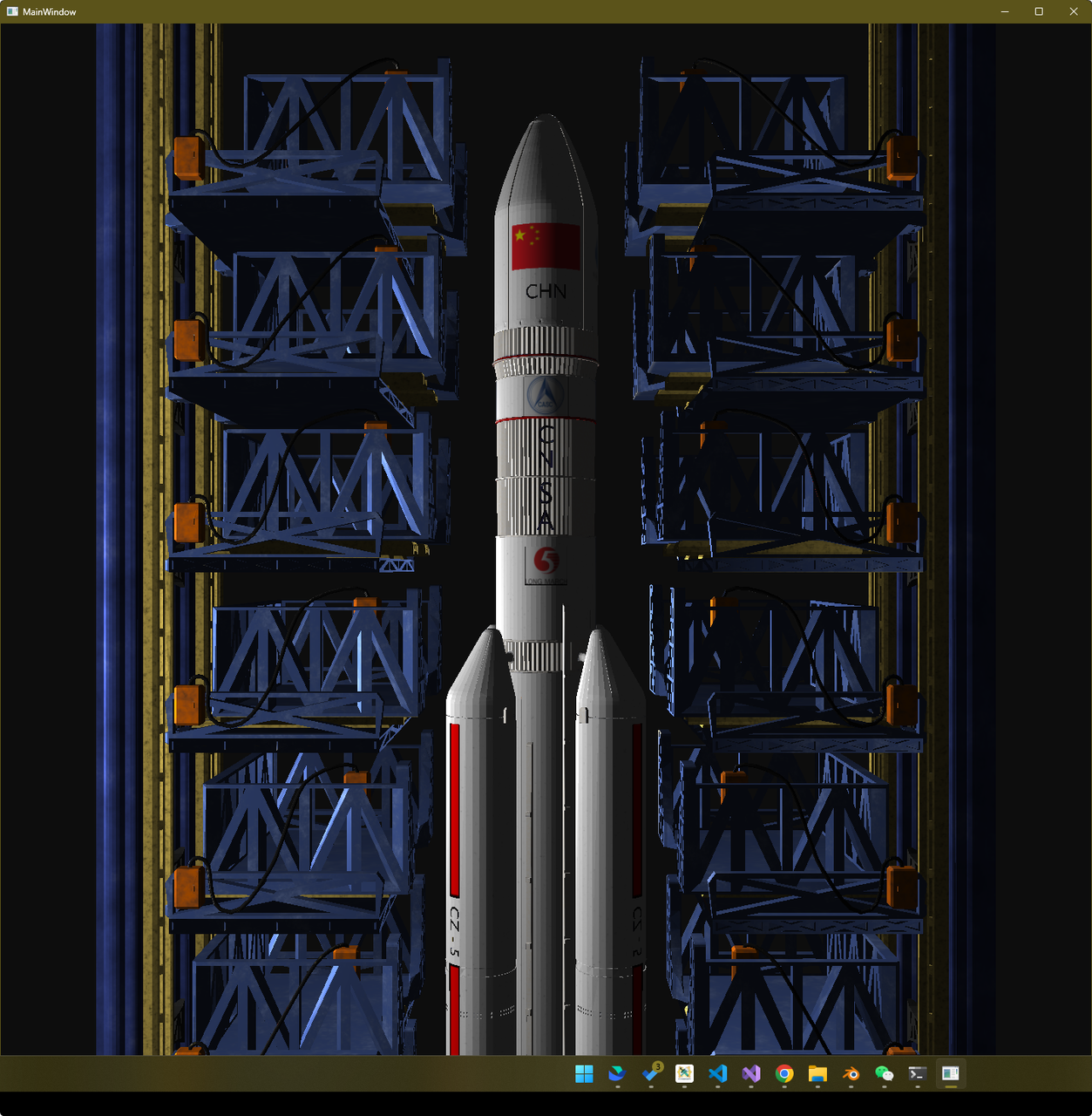
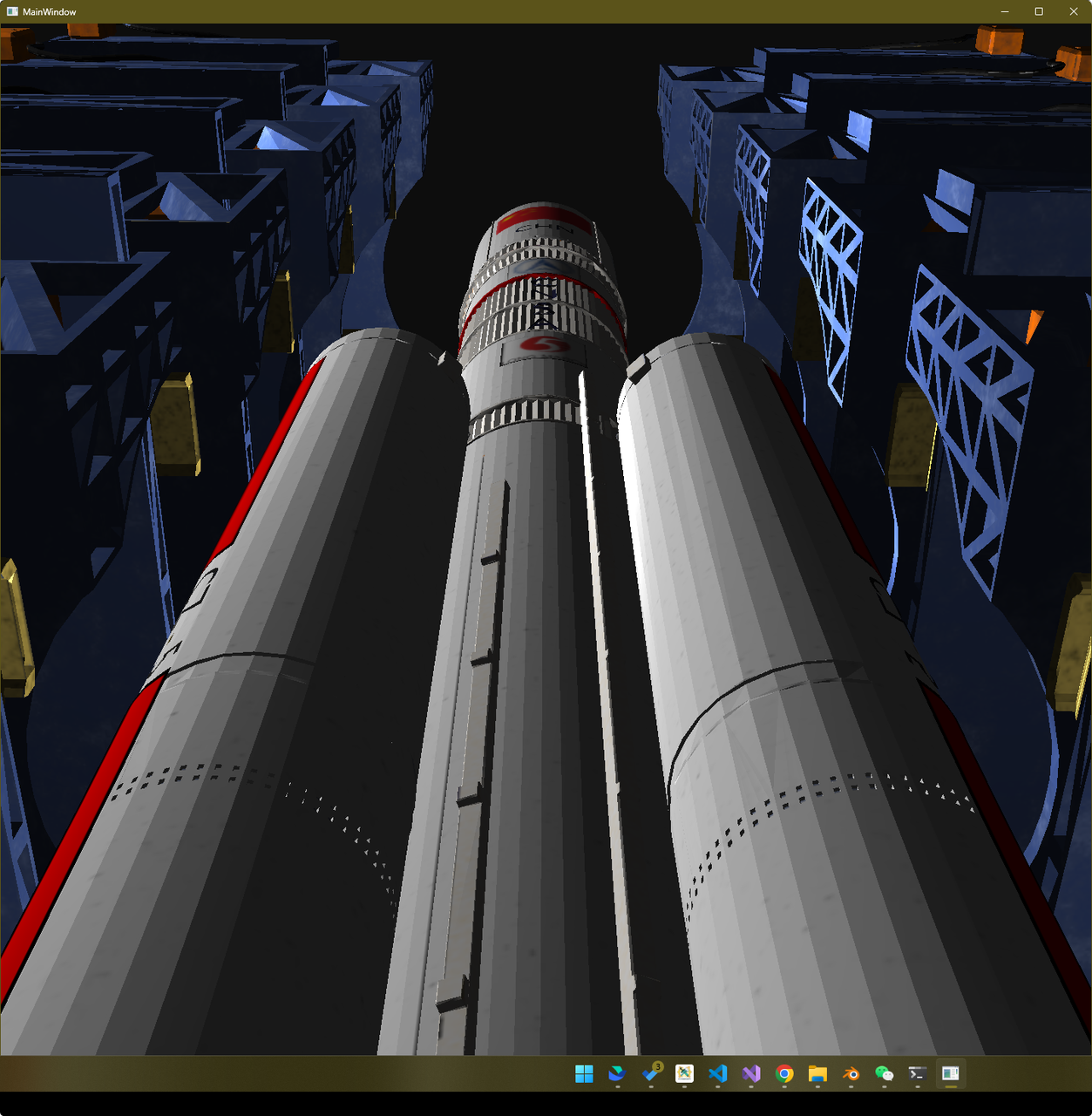
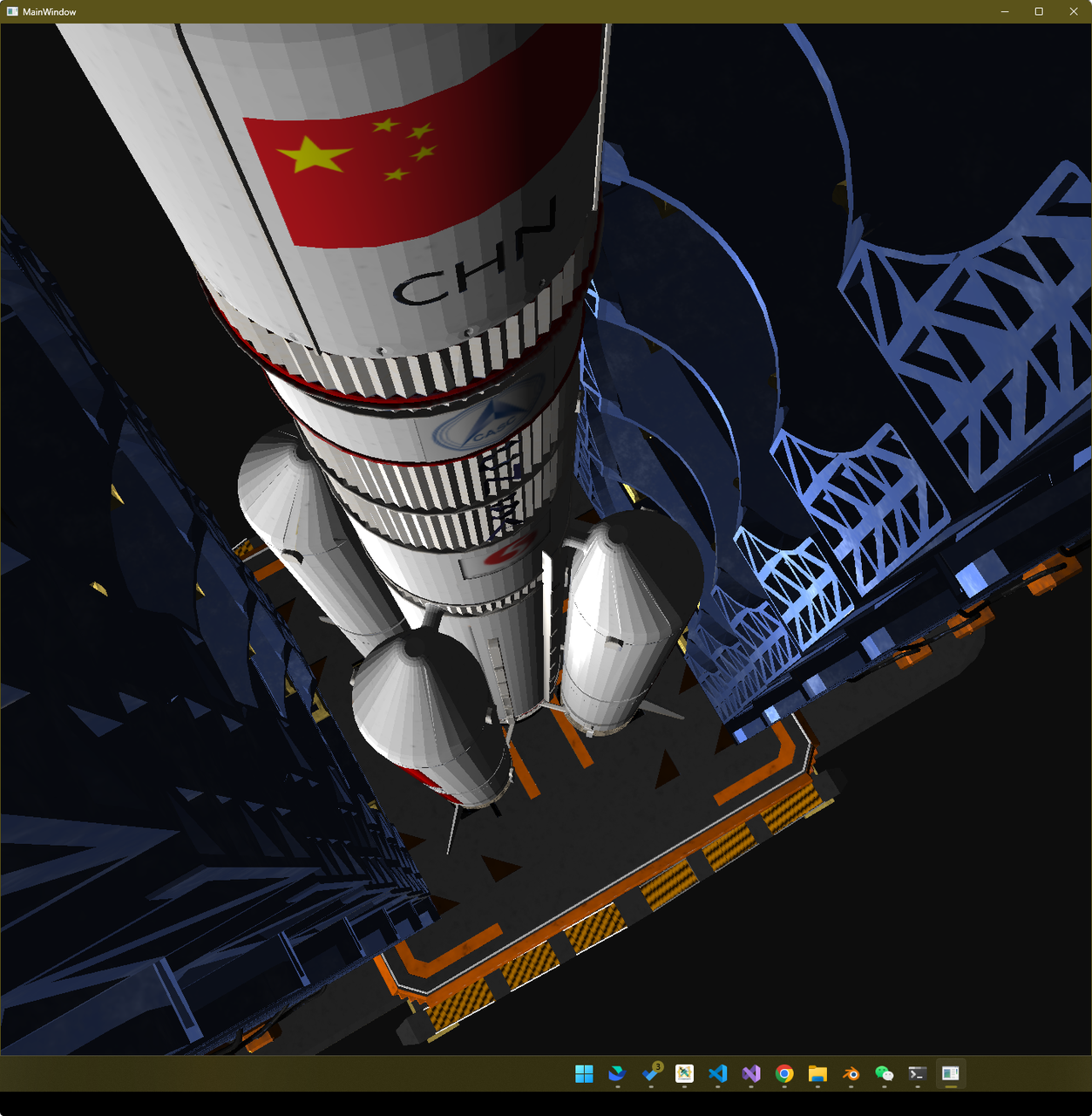
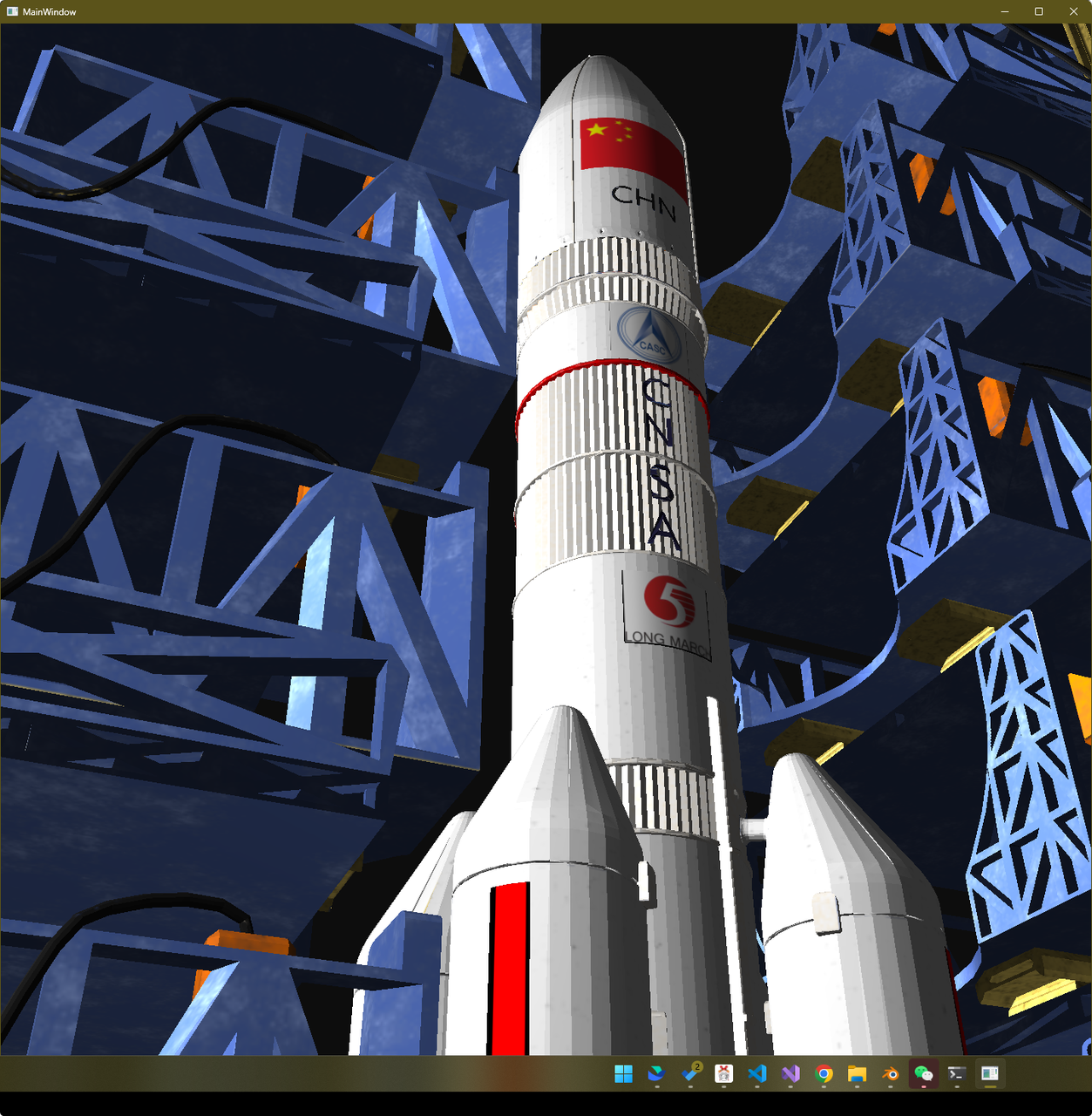
建模 Modeling
由于后续模型导入 OpenGL 中使用Assimp库进行,这一步建模的工作可以使用各种三维软件进行。这里为了方便使用 Blender 进行。
在Blender中建模长征五号运载火箭,并构建材质。最终模型渲染图如下:
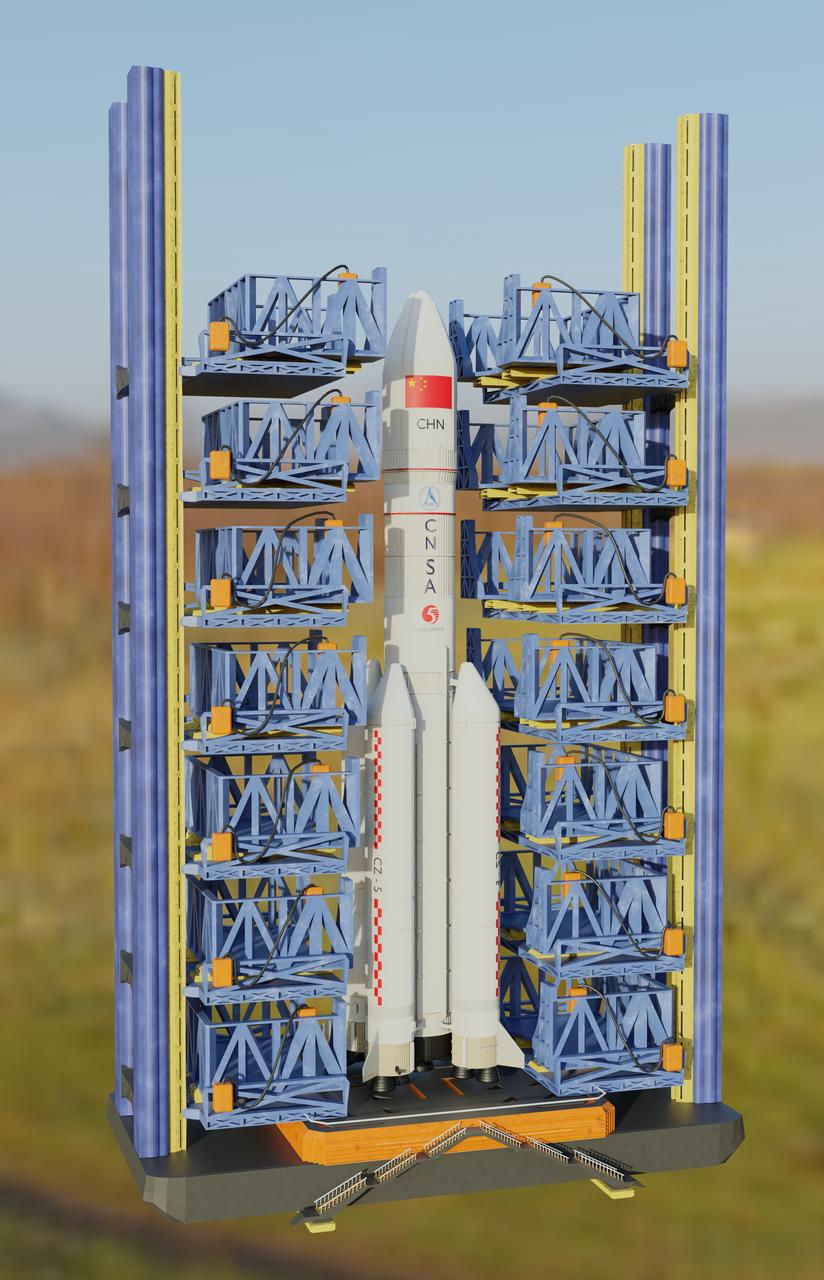

导出为.obj格式的模型文件,以便导入OpenGL中使用。同时会生成.mtl文件来保持模型的材质与贴图信息。
程序初始化 Program Initialization
头文件引用 Includes
为了使项目更加简洁高效,本文使用了多个第三方库来进行各种操作。在主程序最开始需要引用以下内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
#include<iostream> // 标准输入输出
#include<glad/glad.h> // GLAD
#include<GLFW/glfw3.h> // GLFW : Open Source, multi-platform library for OpenGL
// GLM = OpenGL Mathematics
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
#include "stb_image.h" // C++常用图像操作库
// 自定义类
#include "Model.h" // 模型导入类
#include "shaders.h" // Shader 编译
#include "camera.h" // 相机操作类
同时因导入模型需要,还需要安装Assimp,并在Model.h中引用如下内容(详情见文末代码)
1
2
3
#include <assimp/Importer.hpp>
#include <assimp/scene.h>
#include <assimp/postprocess.h>
创建窗口 Create Windows
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
// Parameters
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 1024;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 1024;
const unsigned int VIEW_WIDTH = 1024;
const unsigned int VIEW_HEIGHT = 1024;
// Program Initialize
glfwInit();
// Set OpenGL Version To 4.6 Core
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 4);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 6);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
// For MacOS
#ifdef __APPLE__
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE);
#endif
// Make A Window
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "MainWindow", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
// Init GLAD
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
glViewport(0, 0, VIEW_WIDTH, VIEW_HEIGHT);
任何OpenGL程序都首先需要一个窗口用来展示内容, 这里在main函数最开始首先使用如上代码创建一个窗口用来显示后续的所有内容。这里设置窗口大小为1024*1024。并设置Viewport与窗口大小相同。
设置渲染参数 Set Rendering Parameters
接下来需要设置一些渲染时相关的设置,如深度缓冲(Z-Buffer),以及各种回调函数等。具体代码如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
// Set Call Back Function
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback); // Callback for windows change
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback); // callback for mouse motion
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback); // callback for scrolling-zooming
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED); // callback for keyboard interp
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST); // Open Depth Test
MVP坐标变换 Model - View - Projection Transformtion
MVP坐标变换是计算机图形学中常用的一种坐标变换方法,它由三个矩阵组成:模型矩阵(Model Matrix)、视图矩阵(View Matrix)和投影矩阵(Projection Matrix)。
模型空间 - 世界空间 Model Matrix
模型矩阵用于将模型的局部坐标系变换到世界坐标系中,它包括平移、旋转和缩放等变换操作,将模型放置在世界中的正确位置和方向。
对于本项目来说 Model Matrix 非常的简单,因为仅涉及几个物体。
如下所示,便创建了一个 model 变换矩阵,包含一个平移过程、一个绕Y轴旋转、一个整体缩放 0.5 倍,三个过程。
1
2
3
4
glm::mat4 model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
model = glm::translate(model, glm::vec3(0.0f, -10.0f, 0.0f)); // translate it down so it's at the center of the scene
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(55.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f));
model = glm::scale(model, glm::vec3(0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f));
世界空间 - 相机空间 View Matrix
视图矩阵用于将世界坐标系变换到观察者的坐标系中,它根据观察者的位置和朝向来进行变换,使得观察者能够正确地看到场景中的物体。
这里使用glm库的LookAt()函数来获得到view矩阵:
1
2
3
4
glm::mat4 GetViewMatrix()
{
return glm::lookAt(Position, Position + Front, Up);
}
其中,Front 代表当前视线方向的方向向量。
相机空间 - 投影空间 Projection Matrix
投影矩阵用于将观察者的坐标系变换到裁剪坐标系中,它定义了一个视锥体,将场景中的物体投影到一个二维平面上,以便后续的透视除法和屏幕映射。
这里使用glm库的 perspective() 函数来获得到投影矩阵:
1
2
3
4
5
6
glm::mat4 projection = glm::perspective(
glm::radians(camera.Zoom),
(float)SCR_WIDTH / (float)SCR_HEIGHT,
0.1f,
100.0f
);
其中,FOV参数由后文介绍的Camera类提供,这里当成常量(例如60°),使用glm::radians转换成弧度制。
Aspect Radio 由屏幕长宽之比定义。
最后两个参数为近裁切平面距离与远裁切平面距离。
应用 MVP 变换 Apply MVP Transformation
在 Vertex Shader 中,对模型的顶点坐标按顺序左乘三个变换矩阵来得到更新后的顶点坐标,即完成MVP变换给过程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# version 460 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;
// MVP Matrixes
uniform mat4 model;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 projection;
void main()
{
gl_Position = projection * view * model * vec4(aPos, 1.0);
}
相机操作 Camera Operation
键盘 / 相机运动 Key Board / Camera Movement
为了进行可交互式操作,这里使用键盘用于控制摄像机的三维位置。按键绑定布局使用Unity布局。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window)
{
float cameraSpeed = 2.5f * deltaTime;
float SpeedFactor = 1;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_MOD_SHIFT) == GLFW_PRESS) // Speed UP
SpeedFactor = 2;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS) // Exit
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS) // Forward
camera.ProcessKeyboard(FORWARD, deltaTime, SpeedFactor);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS) // Backward
camera.ProcessKeyboard(BACKWARD, deltaTime, SpeedFactor);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS) // Left
camera.ProcessKeyboard(LEFT, deltaTime, SpeedFactor);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS) // Right
camera.ProcessKeyboard(RIGHT, deltaTime, SpeedFactor);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_E) == GLFW_PRESS) // Up
camera.ProcessKeyboard(UP, deltaTime, SpeedFactor);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_Q) == GLFW_PRESS) // Down
camera.ProcessKeyboard(DOWN, deltaTime, SpeedFactor);
}
鼠标 / 第一人称视角控制 Mouse / First Personal View Control
对于鼠标的控制,首先使用mouse_callback()回调函数获取鼠标输入的偏差值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xposIn, double yposIn)
{
float xpos = static_cast<float>(xposIn);
float ypos = static_cast<float>(yposIn);
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // reversed since y-coordinates go from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
camera.ProcessMouseMovement(xoffset, yoffset);
}
之后处理相机视角更新在Camera类中进行。
首先使用这个函数来将回调函数中获取到的鼠标移动偏差值转换成当前朝向的欧拉角(Euler Angle)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
void ProcessMouseMovement(float xoffset, float yoffset, GLboolean constrainPitch = true)
{
xoffset *= MouseSensitivity;
yoffset *= MouseSensitivity;
Yaw += xoffset;
Pitch += yoffset;
// make sure that when pitch is out of bounds, screen doesn't get flipped
if (constrainPitch)
{
if (Pitch > 89.0f)
Pitch = 89.0f;
if (Pitch < -89.0f)
Pitch = -89.0f;
}
// update Front, Right and Up Vectors using the updated Euler angles
updateCameraVectors();
}
之后使用glm库进行向量计算得到朝向的向量(Front Vector)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
void updateCameraVectors()
{
// calculate the new Front vector
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(Pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(Pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(Pitch));
Front = glm::normalize(front);
// also re-calculate the Right and Up vector
Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Front, WorldUp)); // normalize the vectors, because their length gets closer to 0 the more you look up or down which results in slower movement.
Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Right, Front));
}
再使用LookAt()函数来得到更新后的视角矩阵view
1
2
3
4
glm::mat4 GetViewMatrix()
{
return glm::lookAt(Position, Position + Front, Up);
}
模型导入 Model Import
为了展示更为精细的模型,这里使用Assimp库来进行模型导入的工作。构建一个Model类来导入一个模型文件中的各个Mesh,并创建Mesh类来导入并配置单个模型内的顶点、材质、以及VAO、VBO、EBO还有顶点属性数组等。
光照 Lighting
所有光照的计算均在 Fragment Shader 中进行。
首先接收 Vertex Shader 中传过来的数据,并定义视线和光源的位置向量。以及环境、漫射和高光的强度系数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# version 460 core
in vec2 TexCoord;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec3 FragPos;
out vec4 FragColor; // Final Output For Fragment Shader
uniform vec3 viewPos; // Camera Position
uniform vec3 lightPos; // Point Light Position
uniform sampler2D texture_diffuse1; // Diffuse Texture
uniform sampler2D texture_specular1; // Specular Texture
struct Light {
// Light Strength For 3 Type Of Illuminatings
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
uniform Light light;
Blinn-Phong 光照模型 Blinn-Phong Lighting Model
为了高效率计算光照,这里使用Blinn-Phong光照模型来计算光照效果。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
// 环境光
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * vec3(texture(texture_diffuse1, TexCoord));
// 漫反射
// Calculate Light Vector
vec3 lightDir = normalize(lightPos - FragPos);
// Calculate Diffuse Light Factor For This Frag
float diff = max(dot(Normal, lightDir), 0.0);
// Sample Diffuse Texture
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * (diff * vec3(texture(texture_diffuse1, TexCoord)));
// 镜面反射
// View Vector
vec3 viewDir = normalize(-FragPos);
// Half Vector Between Light Vector And View Vector
vec3 halfwayDir = normalize(lightDir + viewDir);
// Calculate Specular Factor
float spec = pow(max(dot(Normal, halfwayDir), 0.0), 32);
// Sample Specular Texture
vec3 specular = light.specular * (spec * vec3(texture(texture_specular1, TexCoord)));
// 最终颜色
vec3 result = (ambient + diffuse + specular);
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
材质贴图 Textures
贴图采样 Texture Sampler
最终,为了能完整表现模型的表面效果,在Blender中烘焙出模型的漫射贴图与高光贴图并在 Fragment Shader 中应用。
1
2
3
4
uniform sampler2D texture_diffuse1;
uniform sampler2D texture_specular1;
// 使用 texture 函数来采样 2D 贴图
vec3(texture(texture_diffuse1, TexCoord));
资源与参考 Resources And References
Resources
References
https://github.com/JoeyDeVries/LearnOpenGL
代码 Codes
Main.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
#include<glad/glad.h>
#include<GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include<iostream>
#include "shaders.h"
#include "camera.h"
#include "stb_image.h"
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
#include <Model.h>
// settings
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 1440;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 1440;
const unsigned int VIEW_WIDTH = 1440;
const unsigned int VIEW_HEIGHT = 1440;
Camera camera(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f));
float lastX = SCR_WIDTH / 2.0f;
float lastY = SCR_HEIGHT / 2.0f;
bool firstMouse = true;
float deltaTime = 0.0f; // 当前帧与上一帧的时间差
float lastFrame = 0.0f;
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height);
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window);
int main()
{
// Program Initialize
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 4);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 6);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
#ifdef __APPLE__
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE);
#endif
// Make A Window
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "MainWindow", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
// Init GLAD
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
glViewport(0, 0, VIEW_WIDTH, VIEW_HEIGHT);
// Set Call Back Function
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
int nrAttributes;
glGetIntegerv(GL_MAX_VERTEX_ATTRIBS, &nrAttributes);
std::cout << "Maximum nr of vertex attributes supported: " << nrAttributes << std::endl;
// stbi_set_flip_vertically_on_load(true);
// End of Program Initialize
Shader CG_Shader("./Resources/Shaders/Shader.vs", "./Resources/Shaders/Shader.fs");
// Load Model
//Model NanoSuits("./Resources/nanosuit/nanosuit.obj");
Model Rocket("./Resources/Rocket_Real/Rocket_Real.obj");
//Model MoonCar("./Resources/MoonCar/MoonCar.obj");
glm::vec3 lightPos(1.0f, 1.0f, 2.0f);
CG_Shader.use();
CG_Shader.setVec3("lightPos", lightPos);
CG_Shader.setVec3("material.ambient", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
CG_Shader.setVec3("material.diffuse", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
CG_Shader.setVec3("material.specular", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
CG_Shader.setFloat("material.shininess", 32.0f);
CG_Shader.setVec3("light.ambient", 0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f);
CG_Shader.setVec3("light.diffuse", 0.8f, 0.8f, 0.8f); // 将光照调暗了一些以搭配场景
CG_Shader.setVec3("light.specular", 1.2f, 1.2f, 1.2f);
// Start Main Loop
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
// Detect Input
processInput(window);
// Clear Windows
glClearColor(0.05f, 0.05f, 0.05f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
CG_Shader.use();
// Rotate The Light
glm::mat4 LightTrans = glm::mat4(1.0f);
LightTrans = glm::rotate(LightTrans, (float)glfwGetTime() * glm::radians(55.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f));
glm::vec3 lightPos(1.2f, 1.0f, 2.0f);
lightPos = LightTrans * glm::vec4(lightPos,1.0f);
CG_Shader.setVec3("lightPos", lightPos);
glm::mat4 view = camera.GetViewMatrix();
glm::mat4 projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(camera.Zoom), (float)SCR_WIDTH / (float)SCR_HEIGHT, 0.1f, 100.0f);
CG_Shader.setMat4("view", view);
CG_Shader.setVec3("viewPos", camera.Position);
CG_Shader.setMat4("projection", projection);
glm::mat4 model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
model = glm::translate(model, glm::vec3(0.0f, -10.0f, -10.0f)); // translate it down so it's at the center of the scene
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(-90.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f));
model = glm::scale(model, glm::vec3(0.3f, 0.3f, 0.3f)); // it's a bit too big for our scene, so scale it down
CG_Shader.setMat4("model", model);
//NanoSuits.Draw(CG_Shader);
Rocket.Draw(CG_Shader);
// End of Rendering
// Swap Color Buffer
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
// Update Events
glfwPollEvents();
float currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
}
// End Program
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
}
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window)
{
float cameraSpeed = 2.5f * deltaTime;
float SpeedFactor = 1;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_MOD_SHIFT) == GLFW_PRESS)
SpeedFactor = 2;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(FORWARD, deltaTime, SpeedFactor);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(BACKWARD, deltaTime, SpeedFactor);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(LEFT, deltaTime, SpeedFactor);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(RIGHT, deltaTime, SpeedFactor);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_E) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(UP, deltaTime, SpeedFactor);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_Q) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(DOWN, deltaTime, SpeedFactor);
}
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xposIn, double yposIn)
{
float xpos = static_cast<float>(xposIn);
float ypos = static_cast<float>(yposIn);
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // reversed since y-coordinates go from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
camera.ProcessMouseMovement(xoffset, yoffset);
}
// glfw: whenever the mouse scroll wheel scrolls, this callback is called
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
camera.ProcessMouseScroll(static_cast<float>(yoffset));
}
Vertex Shader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# version 460 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aNormal;
layout (location = 2) in vec2 aTexCoord;
out vec2 TexCoord;
out vec3 Normal;
out vec3 FragPos;
uniform mat4 model;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 projection;
void main()
{
gl_Position = projection * view * model * vec4(aPos, 1.0);
TexCoord = aTexCoord;
Normal = aNormal;
FragPos = vec3(model * vec4(aPos, 1.0));
}
Fragment Shader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
# version 460 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec2 TexCoord;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec3 FragPos;
uniform sampler2D Texture1;
uniform sampler2D Texture2;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
uniform vec3 lightPos;
uniform sampler2D texture_diffuse1;
uniform sampler2D texture_specular1;
struct Material {
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float shininess;
};
uniform Material material;
struct Light {
vec3 position;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
uniform Light light;
float specularStrength = 0.7;
void main()
{
// 环境光
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * vec3(texture(texture_diffuse1, TexCoord));
// 漫反射
// Calculate Light Vector
vec3 lightDir = normalize(lightPos - FragPos);
// Calculate Diffuse Light Factor For This Frag
float diff = max(dot(Normal, lightDir), 0.0);
// Sample Diffuse Texture
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * (diff * vec3(texture(texture_diffuse1, TexCoord)));
// 镜面反射
// View Vector
vec3 viewDir = normalize(-FragPos);
// Half Vector Between Light Vector And View Vector
vec3 halfwayDir = normalize(lightDir + viewDir);
// Calculate Specular Factor
float spec = pow(max(dot(Normal, halfwayDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
// Sample Specular Texture
vec3 specular = light.specular * (spec * vec3(texture(texture_specular1, TexCoord)));
// 最终颜色
vec3 result = (ambient + diffuse + specular);
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
// FragColor *= mix(texture(Texture1, TexCoord),texture(Texture2, TexCoord),0.2);
}